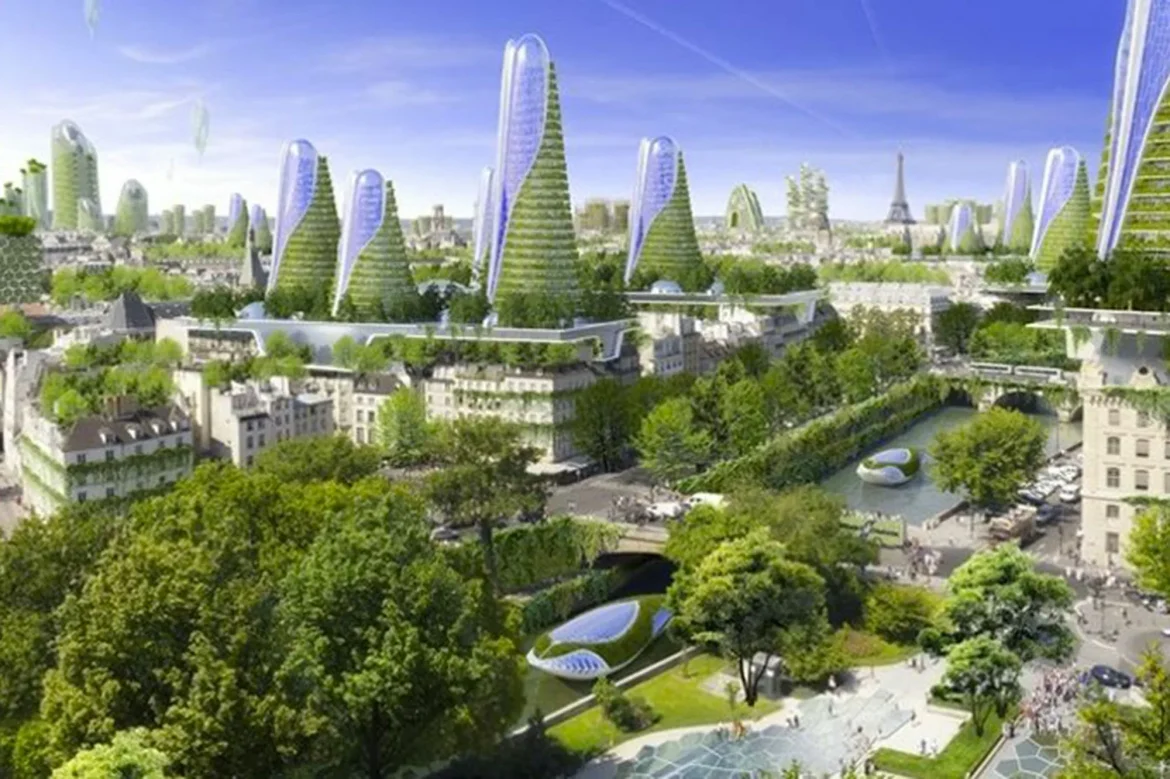
As more than half of the world’s population now lives in cities, urban ecology — the study of ecosystems within metropolitan areas — is gaining importance. Cities may seem distant from “nature,” but they host complex interactions between humans, wildlife, and green spaces that shape both environmental and public health.
Urban areas face unique ecological challenges: air and noise pollution, heat islands, water runoff, and habitat fragmentation. However, they also offer opportunities for sustainable innovation. Green roofs, urban gardens, and eco-parks improve biodiversity, reduce pollution, and enhance residents’ quality of life.